
Nasal Obstruction: Turbinates
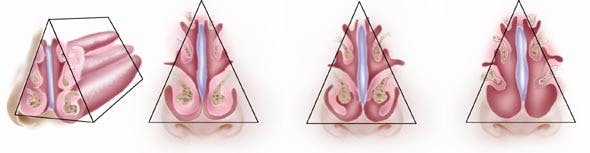
What are turbinates and how do they impact breathing? Turbinates are a normal, anatomic structure in the nose which serve to humidify and filter air. There are three sets of turbinates in the nose. The inferior turbinates (the lowest turbinate shown in picture) is the turbinate responsible for causing nasal blockage. When turbinates are excessively large, they may lead to blockage to one or both sides of the nose.
So what is a turbinate and what purpose does it serve? Turbinates are essentially nasal mucosa covering bone. They normally enlarge and contract to regulate airflow and humidify air. This is really important in drier areas such as the Southwest of the United States.
So why do turbinates get excessively enlarged? Turbinates swell when exposed to allergans, smoke, and pollution. When the swelling is severe enough, the turbinates can actually block airflow from the nose. If the turbinates are swollen for extended period, the patient may have permanently and irreversibly enlarged turbinates. The constant stimulation will cause the bony portion of the turbinate to become enlarged as well as some of the soft tissue of the turbinate itself. The turbinates play a larger role in ethnic nasal obstruction than nasal valves.
Treating turbinate hypertrophy usually starts with a medical approach. Identifying the cause of the turbinate hypertrophy can be useful, particularly if the patient is going to avoid the inciting cause. Sometimes, a nasal spray, such as a nasal steroid or an antihistamine spray can help reduce the size of the turbinate as well. When conservative measures do not work, turbinate surgey can be performed to help restore wide natural breathing.
There are many different techniques to decrease the size of turbinates. The key to turbinate reduction is to reduce the pathologically enlarged portion while maintaining the portion which humidifies and filters air. Cutting out the turbinate will provide the patient with immediate relief (last picture shown on right), at the expense of inability to humidify air and potential problem of persistent nasal crusting afterwards If you have ever traveled to a dry environment, your turbinates are extremely valuable in order to breathe comfortably from your nose by adding moisture to the dry air. Conservative turbinate reduction preserving the mucosa and removing the pathologically enlarged bony portion is my method of choice to improve breathing and maintain normal mucosa.
Turbinate Coblation
Coblation refers to a type of controlled, non-heat driven process that decrease the molecular bonds of tissues to effectively decrease the volume of tissue and can be used to improve nasal obstruction caused by enlarged turbinates.


